


Gastro esophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Overview
 Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is defined as chronic symptoms or mucosal damage produced by the abnormal reflux of stomach acid to the esophagus. A typical symptom is heartburn.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is defined as chronic symptoms or mucosal damage produced by the abnormal reflux of stomach acid to the esophagus. A typical symptom is heartburn.This is commonly due to transient or permanent changes in the barrier between the esophagus and the stomach. This can be due to incompetence of the lower esophageal sphincter, transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxation, impaired expulsion of gastric reflux from the esophagus, or a hiatus hernia. It is condition in which the esophagus becomes irritated or inflamed because of acid backing up from the stomach. The esophagus or food pipe is the tube stretching from the throat to the stomach. When food is swallowed, it travels down the esophagus. The stomach produces hydrochloric acid after a meal to aid in the digestion of food.
- The inner lining of the stomach resists corrosion by this acid. The cells that line the stomach secrete large amounts of protective mucus.
- The lining of the esophagus does not share these resistant features and stomach acid can damage it.
- The esophagus lies just behind the heart, so the term heartburn was coined to describe the sensation of acid burning the esophagus.
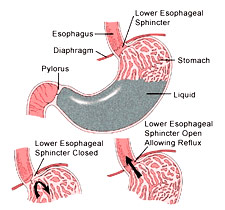
- Normally, a ring of muscle at the bottom of the esophagus, called the lower esophageal sphincter, prevents reflux (or backing up) of acid.
- This sphincter relaxes during swallowing to allow food to pass. It then tightens to prevent flow in the opposite direction.
- With GERD, however, the sphincter relaxes between swallows, allowing stomach contents and corrosive acid to well up and damage the lining of the esophagus. Almost 10% of adults experience GERD weekly or daily. Not just adults are affected; even infants and children can have GERD.
What are the causes of Gastro esophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)?
Top
The cause of GERD is complex. There probably are multiple causes, and different causes may be operative in different individuals, or even in the same individual at different times. The factors that contribute to GERD are the lower esophageal sphincter, hiatal hernias, esophageal contractions, and emptying of the stomach.
The action of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) is perhaps the most important factor (mechanism) for preventing reflux. The following are several contributing factors that weaken or relax the lower esophageal sphincter, making reflux worse:
- Lifestyle - Use of alcohol or cigarettes, obesity, poor posture (slouching)
- Medications - Calcium channel blockers, theophylline (Tedral, Hydrophed, Marax, Bronchial, Quibron), nitrates, antihistamines
- Diet - Fatty and fried foods, chocolate, garlic and onions, drinks with caffeine, acid foods such as citrus fruits and tomatoes, spicy foods, mint flavorings
- Eating habits - Eating large meals, eating soon before bedtime Other medical conditions - Hiatus hernia, pregnancy, diabetes, and rapid weight gain
- Hiatus hernia is a condition when the upper part of the stomach protrudes up above the diaphragm
What are the signs and symptoms of Gastro esophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)?
Top
As GERD can affect both adults and children the sign and symptoms are explained accordingly.
GERD symptoms in adults
Persistent heartburn is the most common symptom of GERD
GERD may be difficult to detect in infants and children. Symptoms may vary from typical adult symptoms. GERD in children may cause repeated vomiting, effortless spitting up, coughing, and other respiratory problems. Inconsolable crying, failure to gain adequate weight, refusing food, bad breathe, and belching or burping is also common. Children may have one symptom or many — no single symptom is universal in all children with GERD. Common symptoms of Pediatric Reflux
Persistent heartburn is the most common symptom of GERD
- Heartburn is a burning pain in the center of the chest, behind the breastbone. It often starts in the upper abdomen and spreads up into the neck.
- The pain can last as long as 2 hours.
- Heartburn is usually worse after eating.
- Lying down or bending over can bring on heartburn or make it worse.
- The pain usually does not start or get worse with physical activity.
- Heartburn is sometimes referred to as acid indigestion.
- Regurgitation of bitter acid up into the throat while sleeping or bending over
- Bitter taste in the mouth
- Persistent dry cough
- Hoarseness (especially in the morning)
- Feeling of tightness in the throat, as if a piece of food is stuck there
- Wheezing
GERD may be difficult to detect in infants and children. Symptoms may vary from typical adult symptoms. GERD in children may cause repeated vomiting, effortless spitting up, coughing, and other respiratory problems. Inconsolable crying, failure to gain adequate weight, refusing food, bad breathe, and belching or burping is also common. Children may have one symptom or many — no single symptom is universal in all children with GERD. Common symptoms of Pediatric Reflux
- Irritability and pain, sometimes screaming suddenly when asleep. Constant or sudden crying or colic-like symptoms. Babies can be inconsolable especially when laid down flat.
- Poor sleep habits typically with arching their necks and back during or after feeding
- Excessive possetting or vomiting
- Frequent burping or frequent hiccups
- Excessive dribbling or running nose
- Swallowing problems, gagging and choking
- Frequent ear infections or sinus congestion
- Babies are often very gassy and extremely difficult to burp after feeds
- Refusing feeds or frequent feeds for comfort
- Night time coughing, extreme cases of acid reflux can cause apnoea and respiratory problems such as asthma, bronchitis and pneumonia if stomach contents are inhaled.
- Bad breath – smelling acidy
- Rancid/acid smelling diapers with loose stool. Bowel movements can be very frequent or babies can be constipated.
- Vomiting feeds.
What are the complications of GERD?
Top
- Ulcers
- Strictures
- Barrett's esophagus
- Cough and asthma
- Inflammation of the throat and larynx
- Inflammation and infection of the lungs
How is GERD Diagnosed?
Top
A detailed historical knowledge is vital for an accurate diagnosis. Useful investigations may include
- Ambulatory Esophageal pH Monitoring,
- Barium swallow
- X-rays,
- Esophageal manometry,
- Endoscopy
What is the role of Homoeopathy in GERD?
As described in the article above GERD has multifactor ail causes. Homoeopathy follows an individualistic approach towards patients suffering from GERD we believe that every individual is different and thus a full in-depth case study is the first step. Then referring to the risk factors the individual was subjected too, a particular line of treatment is adopted. The usual conventional treatment provides only palliation. On the other hand our deep acting constitutional medicine cure the disease in depth rendering the patient free from the disease
A broad criterion of how the homoeopathic medicines act in cases of GERD is mentioned below. The response to treatment can differ from one individual to another patients are advised to consult so that the mode of treatment can be discussed pertaining to their particular case
Relieving Symptoms: Homoeopathic treatment helps in relieving symptoms like
A broad criterion of how the homoeopathic medicines act in cases of GERD is mentioned below. The response to treatment can differ from one individual to another patients are advised to consult so that the mode of treatment can be discussed pertaining to their particular case
Relieving Symptoms: Homoeopathic treatment helps in relieving symptoms like
- Heartburn
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Belching
- Bloating
- Feeling full after only a few bites of food
- Loss of appetite
- Unexplained weight loss
- Pallor, sweating, and rapid (or "racing") heart beat.
- Chest pain or severe stomach pain
- If homoeopathic treatment is sought early it helps in preventing the progress of disease and preventing any complications
- We at DRSS provide our patients with diet charts, exercise schedules and guide them how to modify their lifestyle so that better results can be achieved.
- Our medicines can be started with conventional treatment depending upon the disease state and case.
- Homoeopathic medicines if taken under proper guidance from a well-qualified professional are extremely safe and have no side effects.

Gastro Esophageal Reflux Disease
Related Diseases




