


Gastritis Overview
 Gastritis is an inflammation of the lining of the stomach, and has many possible causes. The main acute causes are excessive alcohol consumption or prolonged use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (also known as NSAIDs) such as aspirin or ibuprofen. Sometimes gastritis develops after major surgery, traumatic injury, burns, or severe infections. Gastritis may also occur in those who have had weight loss surgery resulting in the banding or reconstruction of the digestive tract. Chronic causes are infection with bacteria, primarily Helicobacter pylori.. The most common symptom is abdominal upset or pain. Other symptoms are indigestion, abdominal bloating, nausea, and vomiting. Some may have a feeling of fullness or burning in the upper abdomen. A gastroscopy, blood test, complete blood count test, or a stool test may be used to diagnose gastritis.
Gastritis is an inflammation of the lining of the stomach, and has many possible causes. The main acute causes are excessive alcohol consumption or prolonged use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (also known as NSAIDs) such as aspirin or ibuprofen. Sometimes gastritis develops after major surgery, traumatic injury, burns, or severe infections. Gastritis may also occur in those who have had weight loss surgery resulting in the banding or reconstruction of the digestive tract. Chronic causes are infection with bacteria, primarily Helicobacter pylori.. The most common symptom is abdominal upset or pain. Other symptoms are indigestion, abdominal bloating, nausea, and vomiting. Some may have a feeling of fullness or burning in the upper abdomen. A gastroscopy, blood test, complete blood count test, or a stool test may be used to diagnose gastritis.
What is gastritis?
Top
Gastritis is a condition in which the stomach lining—known as the mucosa—is inflamed. It is not a single disease; rather, gastritis is a condition that has many causes. Common to all people with gastritis is pain or discomfort in the upper part of the belly (abdomen), sometimes called dyspepsia.
The stomach lining contains special cells that produce acid and enzymes, which help break down food for digestion, and mucus, which protects the stomach lining from acid. When the stomach lining is inflamed, it produces less acid, enzymes, and mucus.
Gastritis can be a brief and sudden illness (acute gastritis), a longer-lasting condition (chronic gastritis), if chronic gastritis is not treated, it may last for years or even a lifetime. Gastritis may occur as part of other medical condition.
The stomach lining contains special cells that produce acid and enzymes, which help break down food for digestion, and mucus, which protects the stomach lining from acid. When the stomach lining is inflamed, it produces less acid, enzymes, and mucus.
Gastritis can be a brief and sudden illness (acute gastritis), a longer-lasting condition (chronic gastritis), if chronic gastritis is not treated, it may last for years or even a lifetime. Gastritis may occur as part of other medical condition.
- An example of acute gastritis is stomach upset that may follow the use of alcohol or aspirin.
- Helicobacter pylori is a type of bacteria that infects the stomach. Infection with these bacteria may lead to chronic gastritis.
What are Gastritis Causes?
Top
Gastritis is associated with various medications, medical and surgical conditions, physical stresses, social habits, chemicals, and infections. The causes of gastritis can be divided on its type
Chronic gastritis refers to a wide range of problems of the gastric tissues that are the mostly result of H. pylori infection. Gastritis may also be caused by other medical conditions, including HIV/AIDS, Crohn's disease, certain connective tissue disorders, and liver or kidney failure. Medical and surgical conditions
- Acute
- Chronic
- Medical and Surgical
- Infections
- Alcoholic consumption
- Aspirin (more than 300 drug products contain some form of aspirin)
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen or naproxen)
- Steroids (prednisone is one example)
- Potassium supplements
- Iron tablets
- Cancer chemotherapy medications
- Swallowing poisons or objects
- Corrosives (acid or lye)
- Alcohols of various types
- Swallowed foreign bodies (paper clips or pins)
Chronic gastritis refers to a wide range of problems of the gastric tissues that are the mostly result of H. pylori infection. Gastritis may also be caused by other medical conditions, including HIV/AIDS, Crohn's disease, certain connective tissue disorders, and liver or kidney failure. Medical and surgical conditions
- Physical stress in people who are critically ill or injured
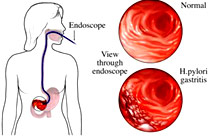
- After medical procedures (such as endoscopy, in which a specialist looks into the stomach with a small lighted tube)
- After an operation to remove part of the stomach
- After radiation treatment for cancer
- Autoimmune diseases
- Pernicious anemia
- Chronic vomiting
- Bacterial
- Tuberculosis
- Syphilis
- Bacterial infections: H pylori infection is the most common. Many other bacteria-even those that usually cause pneumonia or bladder infections-can cause gastritis.
- Viral infections
- Fungal (yeast) infections
- Parasites and worms
What are the signs and Symptoms of Gastritis?
Top
Many people with gastritis experience no symptoms at all. However Symptoms of gastritis do not always correspond to the extent of physical changes in the lining of the stomach, upper central abdominal pain is the most common symptom
- Gastritis pain occurs in the left upper portion of the abdomen and in the back. The pain seems to "go right straight through" a person as it travels from the belly to the back.
- People often use the terms burning, aching, gnawing, or sore to describe the pain. Usually, a vague sense of discomfort is present, but it may occur anywhere from the upper left portion of the abdomen around to the back.
- Nausea
- Vomiting (if present, may be clear, green or yellow, blood-streaked, or completely bloody, depending on the severity of the stomach inflammation)
- Belching (if present, usually does not relieve the pain much)
- Bloating
- Feeling full after only a few bites of food
- Loss of appetite
- Unexplained weight loss
- Pallor, sweating, and rapid (or "racing") heart beat.
- Feeling faint or short of breath
- Chest pain or severe stomach pain
- Vomiting large amounts of blood
- Bloody bowel movements or dark, sticky, very foul-smelling bowel movements
- Any or all of these symptoms can occur suddenly. This is particularly true in adults older than 65 years.
How is the diagnosis of gastritis done?
Top
The most common diagnostic test for gastritis is endoscopy with a biopsy of the stomach.
- Other tests used to identify the cause of gastritis or any complications include the following:
- Upper gastrointestinal (GI) series. The patient swallows barium, a liquid contrast material that makes the digestive tract visible in an x ray. X-ray images may show changes in the stomach lining, such as erosions or ulcers.
- Blood test. The doctor may check for anemia, a condition in which the blood's iron-rich substance, hemoglobin, is diminished. Anemia may be a sign of chronic bleeding in the stomach.
- Stool test. This test checks for the presence of blood in the stool, another sign of bleeding in the stomach.
- Tests for H. pylori infection. The doctor may test a patient's breath, blood, or stool for signs of infection. H. pylori infection can also be confirmed with biopsies taken from the stomach during endoscopy.
What is the role of Homoeopathy in Gastritis?
As described in the article above gastritis has multifactor ail causes. Homoeopathy follows an individualistic approach towards patients suffering from gastritis we believe that every individual is different and thus a full in-depth case study is the first step. Then referring to the risk factors the individual was subjected too, a particular line of treatment is adopted. The usual conventional treatment provides only palliation. On the other hand our deep acting constitutional medicine cure the disease in depth rendering the patient free from the disease
A broad criterion of how the homoeopathic medicines act in cases of gastritis is mentioned below. The response to treatment can differ from one individual to another patients are advised to consult so that the mode of treatment can be discussed pertaining to their particular case
Relieving Symptoms: Homoeopathic treatment helps in relieving symptoms like
Controlling and curing the underlying disease process:It helps by curing the inflammation of the stomach mucosal lining rendering the patient free from disease.
A broad criterion of how the homoeopathic medicines act in cases of gastritis is mentioned below. The response to treatment can differ from one individual to another patients are advised to consult so that the mode of treatment can be discussed pertaining to their particular case
Relieving Symptoms: Homoeopathic treatment helps in relieving symptoms like
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Belching
- Bloating
- Feeling full after only a few bites of food
- Loss of appetite
- Unexplained weight loss
- Pallor, sweating, and rapid (or "racing") heart beat.
- Feeling faint or short of breath
- Chest pain or severe stomach pain
- Vomiting large amounts of blood
- Bloody bowel movements or dark, sticky, very foul-smelling bowel movements
Controlling and curing the underlying disease process:It helps by curing the inflammation of the stomach mucosal lining rendering the patient free from disease.
- If homoeopathic treatment is sought early it helps in preventing the progress of disease and preventing any complications
- We at DRSS provide our patients with diet charts, exercise schedules and guide them how to modify their lifestyle so that better results can be achieved.
- Our medicines can be started with conventional treatment depending upon the disease state and case.
- Homoeopathic medicines if taken under proper guidance from a well-qualified professional are extremely safe and have no side effects.

Gastritis




