


Psoriasis Overview
Psoriasis is a non-contagious common skin condition that causes rapid skin cell reproduction resulting in red, dry patches of thickened skin.
The dry flakes and skin scales are thought to result from the rapid buildup of skin cells. Psoriasis commonly affects the extensor surfaces, skin oflegs elbows, knees, and scalp. But the typical presentation is on the elbows and the knees. Psoriasis can also affect the nails
Psoriasis is a chronic, autoimmune disease it occurs when the immune system sends out faulty signals that speed up the growth cycle of skin cells. Psoriasis is not contagious but can be inherited.
There are five types of psoriasis:
Psoriasis can occur on any part of the body and can be associated with other serious health conditions, such as diabetes, heart disease and depression.
The cause of psoriasis is not known, but it is believed to have a genetic component. Factors such as stress, withdrawal of systemic corticosteroid, excessive alcohol consumption, and smoking sun exposure and HIV infection may affect how often the psoriasis occurs and how long the flare-ups last.
Psoriasis is seen worldwide, in all races, and both sexes. Although psoriasis can be seen in people of any age, from babies to seniors, most commonly patients are first diagnosed in their early adult years.
Psoriasis can be graded as:
The dry flakes and skin scales are thought to result from the rapid buildup of skin cells. Psoriasis commonly affects the extensor surfaces, skin oflegs elbows, knees, and scalp. But the typical presentation is on the elbows and the knees. Psoriasis can also affect the nails
Psoriasis is a chronic, autoimmune disease it occurs when the immune system sends out faulty signals that speed up the growth cycle of skin cells. Psoriasis is not contagious but can be inherited.
There are five types of psoriasis:
- Plaque,
- Guttate,
- Inverse,
- Pustular,
- Erythrodermic.
Psoriasis can occur on any part of the body and can be associated with other serious health conditions, such as diabetes, heart disease and depression.
The cause of psoriasis is not known, but it is believed to have a genetic component. Factors such as stress, withdrawal of systemic corticosteroid, excessive alcohol consumption, and smoking sun exposure and HIV infection may affect how often the psoriasis occurs and how long the flare-ups last.
Psoriasis is seen worldwide, in all races, and both sexes. Although psoriasis can be seen in people of any age, from babies to seniors, most commonly patients are first diagnosed in their early adult years.
Psoriasis can be graded as:
- Mild - Few, scattered, small areas of involvement (about two-thirds of people have mild disease)
- Moderate - More widespread disease affecting larger areas, sometimes affecting the joints
- Severe - Most of the skin surface is affected, sometimes affecting the joints
What are the Causes?
Top
The cause of psoriasis is not fully understood. It is not contagious but those with a family history of psoriasis have an increased chance of having psoriasis. When both parents have psoriasis, the child may have a 50% chance of developing psoriasis
It is a fairly idiosyncratic disease. The majority of people's experience of psoriasis is one in which it may worsen or improve for no apparent reason.
There are two main hypotheses about the process that occurs in the development of the disease.
- The first considers psoriasis as primarily a disorder of excessive growth and reproduction of skin cells. The problem is simply seen as a fault of the epidermis
- The second hypothesis sees the disease as being an immune-mediated disorder in which the excessive reproduction of skin cells is secondary to factors produced by the immune system.
- Injury to the skin
- Sunlight: Most people generally consider sunlight to be beneficial for their psoriasis. However, bad sunburn may worsen psoriasis.
- Streptococcal infections: These bacterial infections have been shown to cause guttate psoriasis, a type of psoriasis that looks like small red drops on the skin
- HIV: Psoriasis typically worsens after an individual has been infected with HIV.
- Drugs: A number of medications have been shown to aggravate psoriasis.
- Lithium –
- Beta-blockers –
- Antimalarials -
- NSAIDS- Drugs, such as ibuprofen
- Emotional stress: Many people see an increase in their psoriasis when emotional stress is increased.
- Smoking: Cigarette smokers have an increased risk of chronic plaque psoriasis.
- Alcohol: Alcohol is considered a risk factor for psoriasis, particularly in young to middle-aged males.
- Hormone changes: The severity of psoriasis may fluctuate with hormonal changes. Disease frequency peaks during puberty and menopause.
- Changes in season and climate.
- Hairspray, some face creams and hand lotions, can also cause an outbreak of psoriasis.
What are the symptoms and signs of Psoriasis?
Top
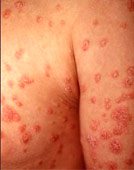 Psoriasis typically looks like red or pink areas of thickened, raised, and dry skin. It classically affects areas over the elbows, knees, and scalp. Essentially any body area may be involved. It tends to be more common in areas of trauma, repeat rubbing, use, or abrasions.
Psoriasis typically looks like red or pink areas of thickened, raised, and dry skin. It classically affects areas over the elbows, knees, and scalp. Essentially any body area may be involved. It tends to be more common in areas of trauma, repeat rubbing, use, or abrasions.
Psoriasis has many different appearances. It may be small flattened bumps, large thick plaques of raised skin, red patches, and pink mildly dry skin to big flakes of dry skin that flake off.
Sometimes pulling of one of these small dry white flakes of skin causes a tiny blood spot on the skin. This is medically referred to as a special diagnostic sign in psoriasis called the Auspitz sign.
Genital lesions, especially on the head of the penis, are common. Psoriasis in moist areas like the navel or area between the buttocks (intergluteal folds) may look like flat red patches.
Scalp, it may look like severe dandruff with dry flakes and red areas of skin. It may be difficult to tell the difference between scalp psoriasis and seborrhea (dandruff).
Variants of psoriasis include
- Plaque,
- Pustular,
- Guttate
- Flexural psoriasis.
Flexural psoriasis (inverse psoriasis): In this form psoriasisappears as smooth inflamed patches of skin. It occurs in skin folds, particularly around the genitals (between the thigh and groin), the armpits, under an overweight stomach, and under the breasts (inframammary fold). It is aggravated by friction and sweat, and is vulnerable to fungal infections.
Guttate psoriasis:numerous small round spots characterize guttate psoriasis. These numerous spots of psoriasis appear over large areas of the body, such as the trunk, limbs, and scalp. Guttate psoriasis is can be associated with streptococcal throat infection.
Pustules psoriasis:In this variant psoriasis appear as raised bumps that are filled with non-infectious pus (pustules). The skin under and surrounding the pustules is red and tender. Pustular psoriasis can be localised, commonly to the hands and feet (palmoplantarpustulosis), or generalised with widespread patches occurring randomly on any part of the body.
Nail psoriasis:It produces a variety of changes in the appearance of finger and toenails. These changes include discolouring under the nail plate, pitting of the nails, lines going across the nails, thickening of the skin under the nail, and the loosening (onycholysis) and crumbling of the nail.
Psoriatic arthritis:It involves joint and connective tissue inflammation. Psoriatic arthritis can affect any joint but is most common in the joints of the fingers and toes. This can result in a sausage-shaped swelling of the fingers and toes known as dactylitis. Psoriatic arthritis can also affect the hips, knees and spine (spondylitis). About 10-15% of people who have psoriasis also have psoriatic arthritis.
How is Psoriasis Diagnosed?
Top
A diagnosis of psoriasis is usually based on the appearance of the skin. There are no special blood tests or diagnostic
procedures for psoriasis.
Sometimes a skin biopsy, or scraping, may be needed to rule out other disorders and to confirm the diagnosis. Another sign of psoriasis is that when the plaques are scraped, one can see pinpoint bleeding from the skin below (Auspitz's sign).
procedures for psoriasis.
Sometimes a skin biopsy, or scraping, may be needed to rule out other disorders and to confirm the diagnosis. Another sign of psoriasis is that when the plaques are scraped, one can see pinpoint bleeding from the skin below (Auspitz's sign).
What is the role of homoeopathy in psoriasis?
Top
Homoeopathic Approach: As described in the article above psoriasis rather than just being a simple skin disease has multifactor ail deep-seated causes like genetic predisposition and faulty immune responses.
Homoeopathy follows an individualistic approach towards patients suffering from psoriasis we believe that every individual is different and thus a full in-depth case study is the first step. Then referring to the risk factors the individual was subjected too, a particular line of treatment is adopted.
The usual conventional treatment provides only mere palliation or suppression through cortisone and immunosuppressant’s. On the other hand our deep acting constitutional medicine cure the disease in depth rendering the patient free from the disease.
A broad criterion of how the homoeopathic medicines act in cases of psoriasis is mentioned below. The response to treatment can differ from one individual to another patients are advised to consult so that the mode of treatment can be discussed pertaining to their particular case.
Relieves Symptoms like:
General malaise (a vague symptom where you feel uncomfortable and a little tired)
Controlling and reversing the underlying Disease process: Our deep acting constitutional medicines work at the root level. They help by addressing the genetic factors and curing the faulty immune response leading to permanent cure. Homoeopathy with its natural medicinal substances used in small quantities cure the disease process without any side effects.
If homoeopathic treatment is sought early it helps in preventing the progress of disease and preventing any complications from occurring, which are usually associated with the disease.
We at DRSS provide our patients with diet charts, exercise schedules and guide them how to modify their lifestyle so that better results can be achieved. Our medicines can be started with conventional treatment depending upon the disease state and case. Homoeopathic medicines if taken under proper guidance from a well-qualified professional are extremely safe and have no side effects.
Psoriasis at a Glance
Homoeopathy follows an individualistic approach towards patients suffering from psoriasis we believe that every individual is different and thus a full in-depth case study is the first step. Then referring to the risk factors the individual was subjected too, a particular line of treatment is adopted.
The usual conventional treatment provides only mere palliation or suppression through cortisone and immunosuppressant’s. On the other hand our deep acting constitutional medicine cure the disease in depth rendering the patient free from the disease.
A broad criterion of how the homoeopathic medicines act in cases of psoriasis is mentioned below. The response to treatment can differ from one individual to another patients are advised to consult so that the mode of treatment can be discussed pertaining to their particular case.
Relieves Symptoms like:
General malaise (a vague symptom where you feel uncomfortable and a little tired)
- Itching
- Skin lesions
- Dryness of skin
- Tenderness
- In cases were joints and nails are effected helps in improving their condition
Controlling and reversing the underlying Disease process: Our deep acting constitutional medicines work at the root level. They help by addressing the genetic factors and curing the faulty immune response leading to permanent cure. Homoeopathy with its natural medicinal substances used in small quantities cure the disease process without any side effects.
If homoeopathic treatment is sought early it helps in preventing the progress of disease and preventing any complications from occurring, which are usually associated with the disease.
We at DRSS provide our patients with diet charts, exercise schedules and guide them how to modify their lifestyle so that better results can be achieved. Our medicines can be started with conventional treatment depending upon the disease state and case. Homoeopathic medicines if taken under proper guidance from a well-qualified professional are extremely safe and have no side effects.
Psoriasis at a Glance
- Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease.
- Psoriasis has no known cause.
- The tendency toward developing psoriasis is inherited in genes.
- Psoriasis is not contagious.
- Psoriasis gets better and worse spontaneously and can have periodic remissions (clear skin).
- Psoriasis is curable with homoeopathic medication.

Psoriasis




