


Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOS) Overview
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome/Disease (PCOS) is one of the most common female endocrine disorders affecting approximately 5%-10% of women of reproductive age (12–45 years old) and is thought to be one of the leading causes of female infertility.
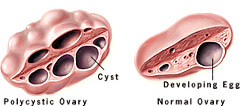
It has been shown that the ovaries of women with PCOS may produce excessive amounts of male hormones, or androgens, which lead to disruptions in the menstrual cycle and impaired fertility. The condition was named because of the finding of enlarged ovaries containing multiple small cysts (polycystic ovaries). Although most women with PCOS have polycystic ovaries, some affected women do not.
The principal features are
The principal features are
- Obesity,
- Irregular menstruation or amenorrhea,
- Acne,
- Effects of androgenic hormones (facial hair)
- Insulin resistance
- Diabetes
What are the causes of Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOS)?
Top
The exact cause(s)of polycystic ovarian syndrome are not clear,It is likely to be the result of a number of both genetic (inherited) as well as environmental factors.
We know now that the characteristic polycystic ovary emerges when a state ofanovulation persists for a length of time. Patients with PCOS have persistently elevated levels of androgens and estrogens, which set up a vicious cycle. Overactive adrenal glands can also produce excess androgens, and these may also contribute to PCOS.
We do know certain Factors that can aggravate or increase the chances of having PCOS are:
We do know certain Factors that can aggravate or increase the chances of having PCOS are:
- Obesity can aggravate PCOS because fatty tissues are hormonally active and they produce estrogen, which disrupts ovulation
- There is some evidence for an inherited (genetic) cause for PCOS, although no specific genetic mutation has been identified as the cause.
- PCOS is also associated with insulin resistance, or an impaired ability to utilize insulin, and this abnormality is also likely related to the cause of PCOS.
What are the sign and symptoms of Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOS)?
Top
The principal signs and symptoms of PCOS are related to menstrual disturbances and elevated levels of male hormones (androgens).But in certain women difficulty in conceiving might be the first reason they come to know about PCOS
Signs and symptoms of PCOS include:
Signs and symptoms of PCOS include:
- Menstrual Irregularities: Delay in normal menstrual cycle (primary amenorrhea), Secondary amenorrhea (absence of menses for more than three months), Scanty menses (oligomenorrhea), this is due to elevated levels of male hormones.
- Acne
- Hirsutism: Excessive hair growth on body.
- Hair loss
- Obesity and weight gain
- Insulin resistance leading to elevated levels of insulin in blood
- Oily skin
- Dandruff
- Infertility this happens due to anovulatory cycles, meaning that women suffering from PCOS do not release an egg every month.
- Skin discoloration
- High Cholesterol levels
- Elevated Blood pressure
- Multiple small cysts in ovaries
What are the complications of Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOS)?
Top
The women suffering from Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome/Disease
(PCOS) are at a higher risk of suffering from many conditions like:
Obesity
Infertility
High Blood pressure
Cancer of uterus (endometrial cancer)
Obesity
Infertility
High Blood pressure
Cancer of uterus (endometrial cancer)
How is Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOS) diagnosed?
Top
 While the diagnosis of PCOS may be suggested by the characteristic symptoms, a number of laboratory tests
can help establish the diagnosis and rule out other conditions that may be responsible for your symptoms.
While the diagnosis of PCOS may be suggested by the characteristic symptoms, a number of laboratory tests
can help establish the diagnosis and rule out other conditions that may be responsible for your symptoms.Blood tests may be performed to evaluate levels of male hormones, such as DHEA and testosterone. Thyroid function may also be evaluated.
Imaging studies such as ultrasound can be safely used to demonstrate the presence of cysts in the ovaries.

Polycystic Ovarian Disease




