Gout overview
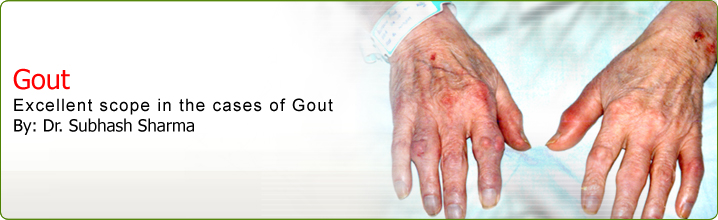
 Gout (also known as podagra when it involves the big toe) is a medical condition usually characterized by recurrent attacks of acute inflammatory arthritis —a red, tender, hot, swollen joint. The metatarsal-phalangeal joint at the base of the big toe is the most commonly affected, in around half of all cases.
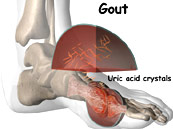
Gout is a condition characterized by an abnormal metabolism of uric acid. People with gout either produce too much uric acid, or more commonly, their bodies have a problem in removing it. There are a number of possible consequences of this buildup of uric acid in the body, including acute and chronic gouty arthritis, kidney stones, and local deposits of uric acid (tophi) in the skin and other tissues. Gout may occur alone (primary gout) or may be associated with other medical conditions or medications (secondary gout).
Gout (also known as podagra when it involves the big toe) is a medical condition usually characterized by recurrent attacks of acute inflammatory arthritis —a red, tender, hot, swollen joint. The metatarsal-phalangeal joint at the base of the big toe is the most commonly affected, in around half of all cases.
Gout is a condition characterized by an abnormal metabolism of uric acid. People with gout either produce too much uric acid, or more commonly, their bodies have a problem in removing it. There are a number of possible consequences of this buildup of uric acid in the body, including acute and chronic gouty arthritis, kidney stones, and local deposits of uric acid (tophi) in the skin and other tissues. Gout may occur alone (primary gout) or may be associated with other medical conditions or medications (secondary gout).Gouty arthritis is a common cause of a sudden onset of a painful, hot, red, swollen joint, particularly in the foot. Gouty arthritis is reportedly the most common cause of inflammatory arthritis in men over the age of 40. It is ultimately diagnosed by detecting uric acid (monosodium urate) crystals in the joint fluid. These uric acid crystals can accumulate over the years in the joint and tissues around the joint, intermittently triggering repeated bouts of inflammation. Repeated "attacks" of gouty arthritis can damage the joint and lead to chronic arthritis. It is caused by elevated levels of uric acid in the blood, which crystallize and are deposited in joints, tendons, and surrounding tissues.
What are the causes of Gout?
Top
Uric acid is generated as the body's tissues are broken down during normal cell turnover. Some people with gout generate too much uric acid (10%). Other people with gout do not effectively eliminate their uric acid into the urine (90%). Genetics, gender, and nutrition (alcoholism, obesity) play key roles in the development of gout.
Gender: Uric acid levels increase at puberty in men and at menopause in women, so men first develop gout at an earlier age (after puberty) than do women (after menopause). Gout in premenopausal women is distinctly unusual
Genetics: If your parents have gout you have 20% more chance of being effected
Lifestyle
Genetics: If your parents have gout you have 20% more chance of being effected
Lifestyle
- Obesity
- Moderate to heavy Alcohol
- Diets rich in red meats, internal organs, yeast, and oily fish increase the risk for gout.
- Physical Trauma
- Starvation and dehydration
- Metabolic Syndrome: A condition involving abdominal obesity, hypertension, insulin resistance, and abnormal lipids
- Renal failure
- Hemolytic Anaemia
- Psoriasis
- Lead Exposure
- Solid organ Transplant
What are the sign and symptoms of gout?
Top
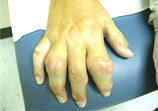
 The first symptom of gouty arthritis is typically the sudden onset of a hot, red, swollen joint. The most common joint involved is at the base of the big toe, but almost any joint can be involved. In some people, the acute pain is so intense that even a bed sheet on the toe causes severe pain. Acute gouty arthritis at the base of the big toe is referred to as podagra.
Patients can develop fever with the acute gout attacks. These painful attacks usually subside in hours to days, with or without medication. In rare instances, an attack can last for weeks. Most patients with gout will experience repeated attacks of arthritis over the years.
Kidney stones are more frequent in people with gout.
The first symptom of gouty arthritis is typically the sudden onset of a hot, red, swollen joint. The most common joint involved is at the base of the big toe, but almost any joint can be involved. In some people, the acute pain is so intense that even a bed sheet on the toe causes severe pain. Acute gouty arthritis at the base of the big toe is referred to as podagra.
Patients can develop fever with the acute gout attacks. These painful attacks usually subside in hours to days, with or without medication. In rare instances, an attack can last for weeks. Most patients with gout will experience repeated attacks of arthritis over the years.
Kidney stones are more frequent in people with gout.Uric acid crystals can form outside joints. Collections of these crystals, known as tophi, can be found in the earlobe, elbow, and Achilles tendon (back of the ankle). Typically, these tophi are not painful but can be a valuable clue for the diagnosis as the crystals that form them can be removed with a small needle for microscopic examination.
How is Gout Diagnosed?
Top
Gouty arthritis is sometimes diagnosed based on the typical clinical presentation in other cases your doctor may advise:
- X rays primarily used to assess underlying joint damage, especially in those who have had multiple episodes of gouty arthritis.
- Blood Examination: A blood sample to look at your cell counts, uric acid levels, kidney function, etc.
- Joint aspiration: The fluid is examined under a microscope to see if there are gout crystals or signs of a bacterial infection present
What is the role of Homoeopathy in GOUT?
Top
As described in the article above gout has multifactor ail causes. Homoeopathy follows an individualistic approach towards patients suffering from gout we believe that every individual is different and thus a full in-depth case study is the first step. Then referring to the risk factors the individual was subjected too, a particular line of treatment is adopted. The usual conventional treatment provides only palliation. On the other hand our deep acting constitutional medicine cure the disease in depth rendering the patient free from the disease
A broad criterion of how the homoeopathic medicines act in cases of gout is mentioned below. The response to treatment can differ from one individual to another patients are advised to consult so that the mode of treatment can be discussed pertaining to their particular case
Relieving Symptoms: Homoeopathic treatment helps in relieving symptoms like
A broad criterion of how the homoeopathic medicines act in cases of gout is mentioned below. The response to treatment can differ from one individual to another patients are advised to consult so that the mode of treatment can be discussed pertaining to their particular case
Relieving Symptoms: Homoeopathic treatment helps in relieving symptoms like
- Joint Pain
- Redness of Joint
- Fever
- If homoeopathic treatment is sought early it helps in preventing the progress of disease and preventing any complications
- We at DRSS provide our patients with diet charts, exercise schedules and guide them how to modify their lifestyle so that better results can be achieved.
- Our medicines can be started with conventional treatment depending upon the disease state and case.
- Homoeopathic medicines if taken under proper guidance from a well-qualified professional are extremely safe and have no side effects.

Gout