


|
Bronchitis Overview
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the air passages within the lungs. It occurs when the trachea (windpipe) and the large and small bronchi (airways) within the lungs become inflamed because of infection or other causes.
Air is pulled into the lungs when we breathe, initially passing through the mouth, nose, and larynx (voicebox) into the trachea and continues en route to each lung via either the right or left bronchi (the bronchial tree - bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli). Bronchi are formed as the lower part of the trachea divides into two tubes that lead to the lungs. As the bronchi get farther away from the trachea, each bronchial tube divides and gets smaller (resembling an inverted tree) to provide the air to lung tissue so that it can transfer oxygen to the blood stream and remove carbon dioxide (the waste product of metabolism).
Bronchitis causes inflammation of the bronchial tubes. The inflammation causes swelling of the lining of these breathing tubes, narrowing the tubes and promoting secretion of inflammatory fluid.
What is bronchitis?
Top
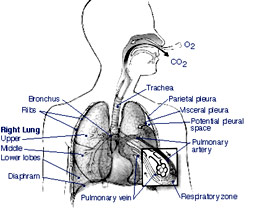 Bronchitis describes inflammation of the bronchial tubes .The inflammation causes swelling of the lining of these breathing tubes, narrowing the tubes and promoting secretion of inflammatory fluid.
Bronchitis can be classified into two categories, acute and chronic, each of which has unique etiologies, pathologies, and therapies. Bronchitis describes inflammation of the bronchial tubes .The inflammation causes swelling of the lining of these breathing tubes, narrowing the tubes and promoting secretion of inflammatory fluid.
Bronchitis can be classified into two categories, acute and chronic, each of which has unique etiologies, pathologies, and therapies.Acute bronchitis is characterized by the development of a cough, with or without the production of sputum, mucus that is expectorated (coughed up) from the respiratory tract. Acute bronchitis often occurs during the course of an acute viral illness such as the common cold or influenza. Viruses cause about 90% of cases of acute bronchitis while bacteria account for less than 10%. Chronic bronchitis, a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, is characterized by the presence of a productive cough that lasts for 3 months or more per year for at least 2 years. Chronic bronchitis most often develops due to recurrent injury to the airways caused by inhaled irritants. Cigarette smoking is the most common cause, followed by air pollution and occupational exposure to irritants, and cold air.
What causes of bronchitis?
Top
Acute bronchitis
What are the symptoms of bronchitis?
Top
Bronchitis Symptoms
Acute bronchitis most commonly occurs after an upper respiratory infection such as the common cold or a sinus infection. You may see symptoms such as fever with chills, muscle aches, nasal congestion, and sore throat.
How is Bronchitis Diagnosed?
Top
Doctors diagnose bronchitis generally on the basis of symptoms and a physical examination.
|

Bronchitis




