|
Overview
Atopic dermatitis (AD is a type of eczema) is an inflammatory, chronically relapsing, non-contagious and a pruritic disease of unknown origin that usually starts in early infancy. Atopic dermatitis is a very common, often chronic (long-lasting) skin disease that affects a large percentage of the world's population. It is also called eczema, dermatitis, or atopy. Most commonly, it may be thought of as a type of skin allergy or sensitivity. The atopic dermatitis triad includes asthma, allergies (hay fever), and eczema. There is a known hereditary component of the disease, and it is seen more in some families. The hallmarks of the disease include skin rashes and itching.
What is atopic dermatitis?
Top
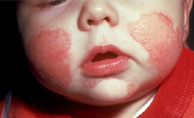 The word "dermatitis" means inflammation of the skin. "Atopic" refers to diseases that are hereditary, tend to run in families, and often occur together. In atopic dermatitis, the skin becomes extremely itchy and inflamed, causing redness, swelling, cracking, weeping, crusting, and scaling. Dry skin is a very common complaint and an underlying cause of some of the typical rash symptoms. The word "dermatitis" means inflammation of the skin. "Atopic" refers to diseases that are hereditary, tend to run in families, and often occur together. In atopic dermatitis, the skin becomes extremely itchy and inflamed, causing redness, swelling, cracking, weeping, crusting, and scaling. Dry skin is a very common complaint and an underlying cause of some of the typical rash symptoms.The skin of a patient with atopic dermatitis reacts abnormally and easily to irritants, food, and environmental allergens and becomes red, flaky and very itchy. It also becomes vulnerable to surface infections caused by bacteria. The skin on the flexural surfaces of the joints (for example inner sides of elbows and knees) are the most commonly affected regions in people. Atopic dermatitis often occurs together with other atopic diseases like hay fever, asthma and conjunctivitis. It is a familial and chronic disease and its symptoms can increase or disappear over time. Atopic dermatitis in older children and adults is often confused with psoriasis. Atopic dermatitis afflicts humans, particularly young children; it is also a well-characterized disease in domestic dogs.
What is the difference between atopic dermatitis and eczema?
Top
Eczema is used as a general term for many types of skin inflammation (dermatitis) and allergic-type skin rashes. There are different types of eczema, like allergic, contact, irritant, and nummular eczema. Several other forms have very similar symptoms. Atopic dermatitis is typically a more specific set of three associated conditions occurring in the same person including eczema, allergies, and asthma. Not every component has to be present at the same time, but usually these patients are prone to all of these three related conditions.
What are the causes of AD?
Top
The cause of atopic dermatitis is not known, but the disease seems to result from a combination of genetic (hereditary) and environmental factors. There seems to be a basic hypersensitivity and an increased tendency toward itching. While emotional factors and stress may in some cases exacerbate or initiate the condition, they do not seem to be a primary or underlying cause for the disorder.
What are symptoms of Atopic dermatitis?
Top
No. Atopic dermatitis itself is definitely not contagious and it cannot be passed from one person to another through skin contact. There is generally no cause for concern in being around someone with even an active case of atopic dermatitis, unless they have active skin infections. Atopic Dermatitis At A Glance
|

Atopic Dermatitis