


|
What is Aplastic Anaemia
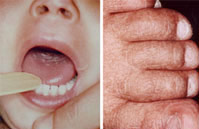 Aplastic anemia is a condition where bone marrow does not produce sufficient new cells to replenish blood cells. The condition, per its name, involves both aplasia and anemia. Typically, anemia refers to low red blood cell counts, but aplastic anemia patients have lower counts of all three blood cell types: red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, termed pancytopenia.
Aplastic anemia is a condition where bone marrow does not produce sufficient new cells to replenish blood cells. The condition, per its name, involves both aplasia and anemia. Typically, anemia refers to low red blood cell counts, but aplastic anemia patients have lower counts of all three blood cell types: red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, termed pancytopenia.Aplastic anemia is a syndrome of bone marrow failure characterized by peripheral pancytopenia and marrow hypoplasia, and mild macrocytosis is observed in association with stress erythropoiesis and an elevated fetal hemoglobin levels.
Signs and symptoms
Top
Causes
Top
In many cases, the etiology is considered to be idiopathic (cannot be determined), but one known cause is an autoimmune disorder in which white blood cells attack the bone marrow.
Aplastic anemia is also sometimes associated with exposure to toxins such as benzene, or with the use of certain drugs,including chloramphenicol, carbamazepine, felbamate, phenytoin, quinine, and phenylbutazone. Many drugs are associated with aplasia mainly according to case reports but at a very low probability. As an example, chloramphenicol treatment is followed by aplasia in less than 1 in 40,000 treatment courses, and carbamazepine aplasia is even rarer. Exposure to ionizing radiation from radioactive materials or radiation-producing devices is also associated with the development of aplastic anemia.
Homoeopathic medicines act by
Top
Relieving the symptoms: It helps by initiating the process of cell production and thus relieving and controlling the disease process
Preventing exacerbations (attacks): It helps in preventing any further bleeding episodes which are usually associated with aplastic anemia. Controlling the disease process: Our homoeopathic medicines can be started with conventional medicines depending upon the stage of the disease. |

Aplastic Anemia




