The term
Trigeminal
Neuralgia
(TN),
has two
words
within
it.
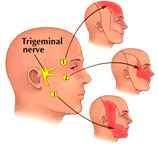
Trigeminal
nerve is
one of
the
(twelve)
cranial
(head)
nerves
which
has
three
divisions
(ophthalmic,
maxillary,
and
mandibular)
supplying
to the
areas of
upper
eye-lid
to the
lower
chin.
Neuralgia
means
pain. TN
is a
disorder
of the
Trigeminal
nerve
which
presents
as
facial
pain and
headache.
The pain
is
characteristically
severe,
intense,
sharp,
episodic,
periodical,
excruciating,
stabbing
and
short
lasting.
Trigeminal
nerve is
the
largest
of
twelve
cranial
nerves.
All
sensations
from the
face and
mouth
are
covered
by the
Trigeminal
nerve.
One of
the
branches
of the
Trigeminal
is often
injected
by your
dentist
while
working
on your
dental
cavity.
|
TN is
also
known as
tic
douloureux.
When the
patient's
Trigeminal
nerve
during
an acute
neuralgia
phase
was
studied
under
electron
microscope,
it was
revealed
that the
abnormality
existed
at the
level of
the
inner
nerve
fibers
called
axons
which
carry
nerve
sensation,
as well
as the
myelin
(the
nerve
lining
covering
the
nerve
fibers).
Due to
the
damage
to such
delicate
parts,
the
nerve
fiber
behave
like
electrical
wire
with
open
ends,
leading
to
electric
shock
like
pain
induced
by touch
or jerk.
|
 |
|
|
|
What
causes
Trigeminal
Neuralgia?
The
causes
of TN
are
explained
in
detail
on a
separate
page. In
short,
it has
been
increasingly
proved
and
understood
that
most
cases of
TN have
demyelination
of the
sensory
nerve
fibers
of the
Trigeminal
Nerve,
either
in the
nerve
root or
(rarely)
the
brain
stem.
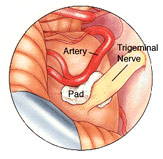
Demyelination means an erosion of the nerve sheath, which leads to the exposure of the nerve fibers.The
exposed
nerve
fibers
often
get
compressed
or
irritated
by blood
vessels
(pulsating
arteries
or
veins),
which
lead to
painful
episodes
of
Trigeminal
Neuralgia. |
|
|
|
|
Click
here for Case
Studies |
|
|




















