Gout is
a form
of
arthritis
which is
caused
by the
accumulation
of uric
acid
crystals
in
joints.
In this
condition,
due to a
metabolic
dysfunction,
there is
deposition
of uric
acid in
and
around
the
joints
causing
severe
painfulness,
swelling
and
restricted
mobility
of the
affected
joint.
|
|
Causes:
The
underlying
cause of
gout is
a
disturbance
in
Purine
metabolism
of the
body.
Purine
is a
substance
found
plenty
in the
living
cells as
well as
in many
food
articles.
Uric
acid is
a body
waste
product,
which is
produced
in the
body
after
the
breakdown
of
Purine.
Underexcretion of uric acid through the kidneys and large intestines or excess formation of uric acid |
|
due to
certain
factors
(such as
alcohol,
lack of
physical
activity,
crash
diet,
meat,
etc.)
leads to
accumulation
of
excess
uric
acid in
the
blood,
eventually
leading
to Gout.
The
exact
cause
for the underexcretion
remains
unknown
in many
cases,
and it
is
believed
to be
more
genetically
determined.
Symptoms:
Gout is
an
intensely
painful
condition,
which
mostly
affects
only one
joint (monoarthritis)
at a
time,
most
commonly
the big
toe.
However,
Gout may
also
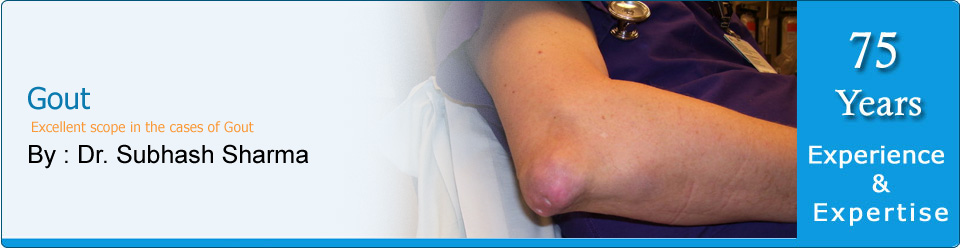
affect
elbows,
knees,
ankles,
wrists
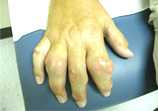
or small
joints
of the
hands
and
feet.
The
classic
history
in a
patient
suffering
from
Gout is
of
excruciating
and
sudden
pain,
swelling,
redness,
warmth
and
stiffness
of the
joint.
Low-grade
fever
may also
be
present.
The skin
overlying
the
joint
can also
be
swollen,
tender
and sore
if it is
touched
even
lightly.
Patients
with
longstanding
hyperuricemia
(high
levels
of uric
acid in
blood)
can have
uric
acid
crystal
deposits
called
tophi in
other
tissues
as well,
e.g. the
helix of
the ear.
Gout
has four
distinct
stages:
Asymptomatic:
High
levels
of Uric
acid in
blood
but no
joint
complaints
Acute
phase:
Acute
complaints
described
above
occur
for a
brief
period
Intercritical
phase:
There is
no pain
or
swelling
of
joints
in this
phase,
the
patient
is
relatively
symptom-free.
Chronic:
Gout
attacks
may
become
frequent
during
this
phase
and the
condition
may
affect
many
joints
at a
time (polyarticular).
Tophi
formation
may also
be seen.
|
Suggestion
about
homeopathic
treatment:
Having understood that Gout is caused by the constitutional factors, it calls for constitutional approach towards its treatment. The constitutional approach involves evaluation of the individual factors inclusive of one's personal and family history (ascertaining the genetic tendency), while planning a long-term treatment. Homeopathic approach to Gout treatment is more of a totalistic approach. Homeopathy helps in controlling the |

|
|
|
pain
during
the
acute
attack
of gout
as well
as helps
in
preventing
the
recurrence
of such
episodes.
It helps
in
reducing
stiffness
and
improves
the
mobility
of the
joints.
Homeopathy
is very
strongly
suggested
for the
treatment
of Gout. |
|
|
|
Click
here for Case
Studies |
|
|