Gastro-esophageal
reflux
disease
or
acid-reflux
disease
is a
condition
in which
the
contents
of the
stomach
reflux
backwards
into the
esophagus
(food
pipe).
Since
the
stomach
contents
are
acidic
in
nature,
this
damages
the
inner
lining
of the
food
pipe and
causes
symptoms
of
heartburn,
pain,
etc.
|
Some
amount
of
reflux
of
stomach
contents
is
normal
in all
individuals
but not
everyone
develops
GERD.
The main
reason
behind
this is
that
only in
some
individuals
this
refluxed
fluid is
more
acidic
and
remains
in the
esophagus
for
longer
duration
thus
causing
GERD.
Dietary
causes
and
certain
faulty
habits
are
frequently
responsible
for
initiating
this
condition
in
individuals
who are
prone to
develop
it.
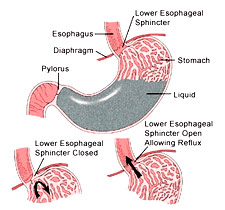
At the junction of the food pipe (esophagus) and the stomach is a muscular gateway (called lower esophageal sphincter or LES). Under normal circumstances, this sphincter remains contracted
so that
no
contents
of the
stomach
can go
back
into the
esophagus
but when
this
sphincter
becomes
relaxed
due to
any
reason
or is
weak,
it
may
allow
the
contents
of the
stomach
to flow
back
into the
esophagus
causing
inflammation
of the
lining
of the oesophagus.
There
can also
be many
other
causes
of GERD
which
will be
discussed
in
details
later. |
 |
|
|
Gerd
in
Childen
GERD is
not an
uncommon
disorder
amongst
infants
but this
diagnosis
is
frequently
missed
out due
to the
fact
that
spitting
up after
a meal
is a
common
occurrence
in
children.
However,
this is
a
difference
between
spitting
up after
a meal
and the
symptoms
of GERD.
If the
parents
are able
to
observe
that
their
infant
possibly
has
symptoms
that are
not
normal,
they
will
seek
treatment
well in
time.
GERD
causes
upward
movement
of the
contents
of the
stomach
(food+acid)
into the
food-pipe
(esophagus)
of the
child,
sometimes
into or
out of
the
mouth.
Causes
of GERD
in
children
Symptoms
of GERD
Consult
your
health
care
provider
when
following
occurs
Diagnosis
of GERD
in
children
Treatment
of GERD
in
children
Causes
of GERD
in
children:
A poorly
coordinated
gastro-intestinal
tract is
the
commonest
cause of
GERD in
children.
An
immature
digestive
system
is the
prime
reason
for this
complaints
and this
is
precisely
why most
of the
infants
outgrow
this
condition
by the
time
they
complete
1 year
of age.
The
causes
of GERD
in older
children
are
predominantly
the same
as the
causes
of GERD
in
adults.
Certain
other
factors
that may
contribute
to GERD
include
obesity,
overfeeding,
certain
medications,
etc.
There
also
appears
to be an
inherited
component
to GERD,
as it is
more
common
in some
families
than in
others.
Symptoms
of GERD:
The
common
symptoms
of GERD
in
children
are as
follows:
Recurrent
vomiting
Frequent
or
persistent
cough
Refusing
feeds or
notable
difficulty
in
eating
Choking
or
gagging
during
feeds
Older
children
may
complain
of
heartburn,
abdominal
pain,
gas
Infants
may
demonstrate
colicky
behavior
(frequent
crying
and
fussiness).
Regurgitation
and
re-swallowing
Severe
cases
may lead
to any
of the
following
in the
long
run:
Poor
growth
Breathing
problems
Recurrent
pneumonia
Consult
your
health
care
provider
when
following
occurs
Large or
persistent
vomiting,
particularly
in
infants
under 2
months
of age
Vomiting
of fluid
that is
greenish,
yellowish,
appears
like
grounded
coffee
or blood
Difficult
breathing
associated
with
vomiting
or
spitting
up
Excessive
irritability
related
to
feeding
Weight
loss or
poor
weight
gain
associated
with
refusal
to feed.
Difficult
or
painful
swallowing
Diagnosis
of GERD
in
children:
In most
of the
cases,
the
history
given by
the
parents
is
sufficient
enough
to
diagnose
this
condition.
Repeated
recurrence
of the
above-mentioned
complaints
and
visible
distress
of the
child
are
adequate
for
diagnosis.
However,
following
tests
can be
conducted
to
confirm
the
diagnosis
Upper GI
endoscopy
Barium
swallow
Gastric
emptying
study
Esophageal
pH probe
Treatment
of GERD
in
children:
Most
babies
outgrow
GERD by
the time
they
complete
one year
of age.
However,
even
during
this
period,
proper
treatment
must be
administered
to
ensure
that the
complaints
do not
worsen.
For
children
in whom
this
condition
persists
beyond
one year
of age,
the
treatment
gives
significant
relief
from
distress
and also
controls
the
progress
of the
complaints.
Click
here to
read
about
the
Homeopathic
treatment
of GERD
in
children.
Please
note
that the
principles
of
treatment
largely
remain
the same
as in
adults.
However,
certain
additional
life-style
changes
are
suggested
for
infants
for
better
control
of the
symptoms:
Elevate
the head
end of
the
baby's
crib
Hold the
baby
upright
for at
least 30
minutes
after a
feed.
Burp
feeding
on each
side.
Try
several
short
feeds
frequently
rather
than one
large
feed
With the
approval
of your
doctor,
introduce
semi-solid
foods
into the
diet of
your
infant
Avoid
over-feeding
the
child at
any time
Older
children
should
not be
allowed
to lie
down for
at least
2 hours
after
meals
Limit
foods
that you
think
worsen
your
child's
complaints
|
|
|
|
Click
here for Case
Studies |
|
|