|
Atopic
dermatitis
is an immune
meditated
inflammation
of the skin,
often with a
significant
genetical
component.
Pruritus
(itching) is
the primary
symptom;
skin lesions
range from
mild
erythema to
severe
lichenification. |
|
AD primarily affects children in urban
areas or developed countries. Like asthma, it may be linked
to pro-allergic/pro-inflammatory T-cells immune response.
Such responses are becoming more common in developed
countries, because trends toward smaller families, cleaner
indoor environment, and early use of vaccination and
antibiotics deprive children of early exposure to infection
and allergens that suppress pro-allergic T cells and induce
tolerance. |
 |
|
 |
AD
occurs
when
environmental
exposure
triggers
immunologic,
usually
allergic,
in
generally
susceptible
people.
Common
environmental
triggers
include
foods
(e.g.
Milk,
eggs,
soy,
wheat,
peanuts,
fish),
airborne
allergens
(e.g.
dust
mites,
molds,
dander),
and
staphylococcus
aureus
colonization
on
skin
due
to
deficiencies.
AD
is
common
within
families,
suggesting
a
genetic
component. |
|
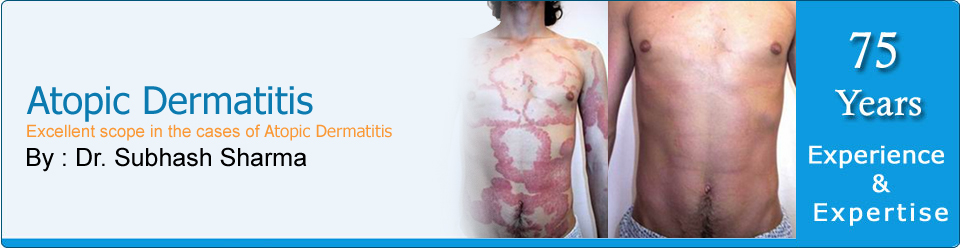
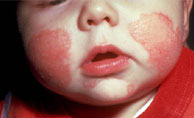
Symptoms and
Signs:
AD usually appears
in infancy,
typically by 3month.
In the acute phase,
lasting 1 to 2
month, red, weeping,
crusted lesions
appear on the face
and spread on the
neck, scalp,
extremities, and
abdomen. In the
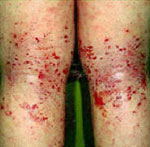
chronic phase,
scratching and
rubbing create skin
lesions (typically
erythematous macules
and papules that
lichenify with
continued
scratching)
Patients have a
threshold for
perceiving itch, and
itch worsens with
allergen exposures,
dry air, sweating,
local irritation,
wool garments, and
emotional stress.
AD may become
generalized.
Secondary bacterial
infections and
regional
lymphadenitis are
common.
During the course of
the disease there
may be periods when
the disease becomes
worse; such periods
are called flare-ups
or exacerbations.
Then there may also
be periods when the
skin symptoms
improve or clears up
completely and such
periods are called
remissions.
Frequent use of
topical products
exposes the patient
to many potential
allergens, and
contact dermatitis
may aggravate and
complicate AD, as
may the generally
dry skin that is
common in these
patients. |
Homoeopathic
Approach
Homoeopathic
treatment is
strongly recommended
in Asthma. |
|
Homoeopathic
medicines act by: |
- Relieving
the symptoms
- Preventing
exacerbations
(attacks)
- Controlling
and curing the
disease process
|
Relieving the
symptoms:
Homoeopathic medicines offer considerable relief symptoms of Atopic dermatitis patients like itching, papules. |
Preventing
exacerbations
(attacks):
Homoeopathic
medicines prevent
any exacerbations at
fist prolonging the
time between
episodes and later
preventing their
occurrence leading
to permanent cure. |
Controlling and
curing the disease
process:
Homoeopathic
medicines offer
permanent cure in AD
they act by
enhancing the
individual’s immune
response against
allergens, thus
producing stronger
immunity so as to
decrease
inflammation caused
by a variety of
triggering stimuli.
AD development is
multifactorial and
depends upon
interaction between
susceptible genes
and environmental
factors. Thus
homoeopathy with its
deep acting
constitutional
remedies offers
excellent results.
Our medicines have
not to be taken for
life time. Once
cured the patients
develops immunity
towards the
triggering stimulus
which is maintained
even after
medication is
stopped.
It also helps in
preventing
occasional features
which develop along
with long standing
AD Like:
Cataracts, facial
Erythema, Food
Intolerance, Nipple
eczema, Recurrent
Conjunctivitis, Wool
Intolerance etc.
|
Click
here for Case
Studies
|
|